- Q What is BLDC Power Roller’s IP rating?
- A
Stainless steel cladding tube: IP52.
- Q How about the lead time for both bearings and power rollers?
- A
In normal arrangement of production, the lead time will be set approximately 60 days after confirm order. The lead time can be adjustable by the quantity, production control, and quantity of ongoing orders. Therefore, if you have any issues on the lead time arrangement, please contact our sales for negotiation.
- Q Bearing Internal Clearance
- A
Bearing Internal Clearance
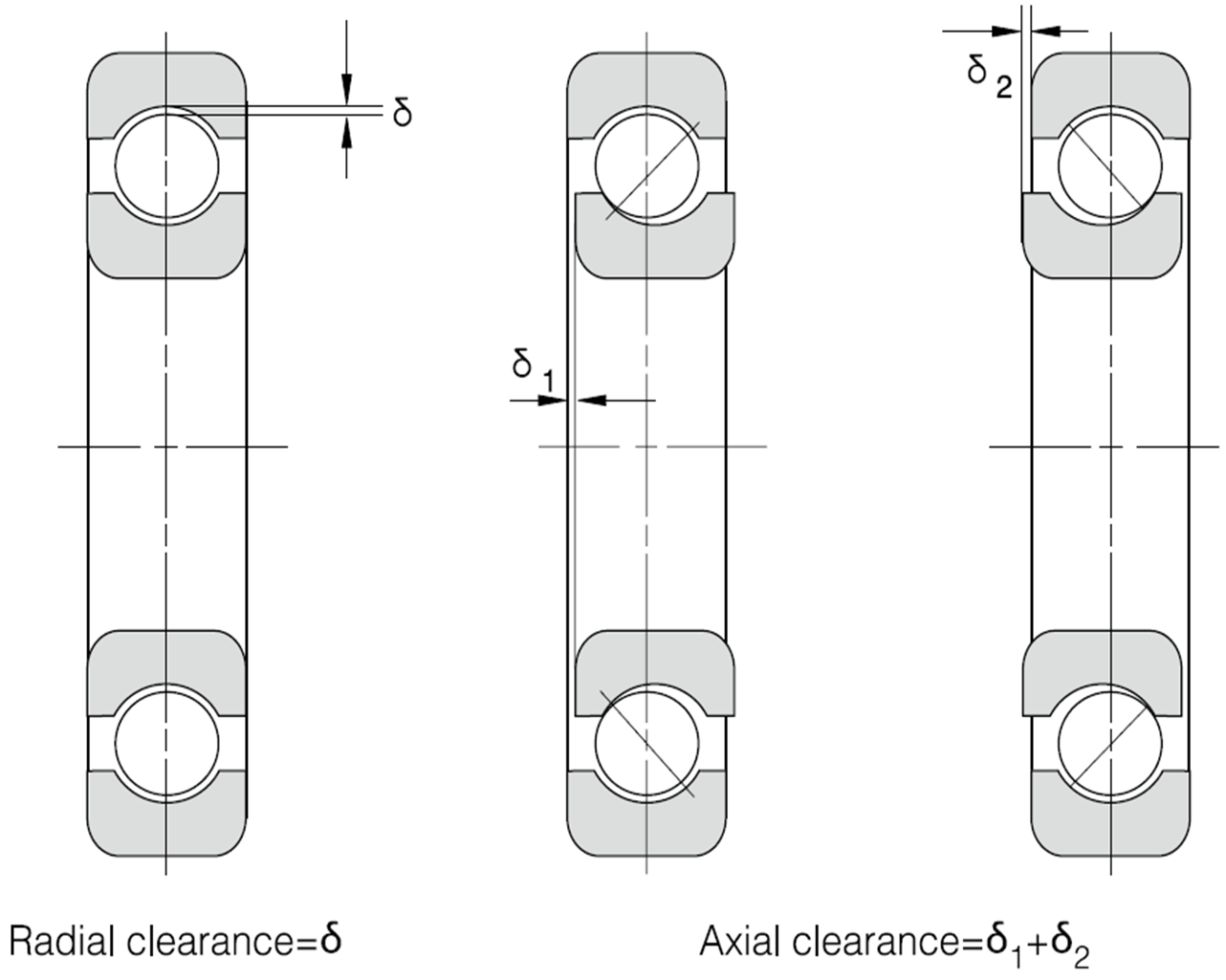
Bearing internal clearance is the amount of internal free movement before mounting.
As shown in Fig.1, when either the inner ring or the outer ring is fixed and the other ring is free to move, displacement can take place in either an axial or radial direction. This amount clearance and, depending on the direction, is called the radial internal clearance or the axial internal clearance.
Fig. 1 Internal Clearance
Internal Clearance Selection
The internal clearance of a bearing under operating conditions (effective clearance) is usually smaller than the same bearing's initial clearance before being installed and operated. This is due to several factors including bearing fit, the difference in temperature between the inner and outer rings, etc. As a bearing's operating clearance has an effect on bearing life, heat generation, vibration, noise, etc; care must be taken in selecting the most suitable operating clearance.
Table 1 Examples of applications where bearing clearances other than CN (nomal) clearance are used (Unit: µm)
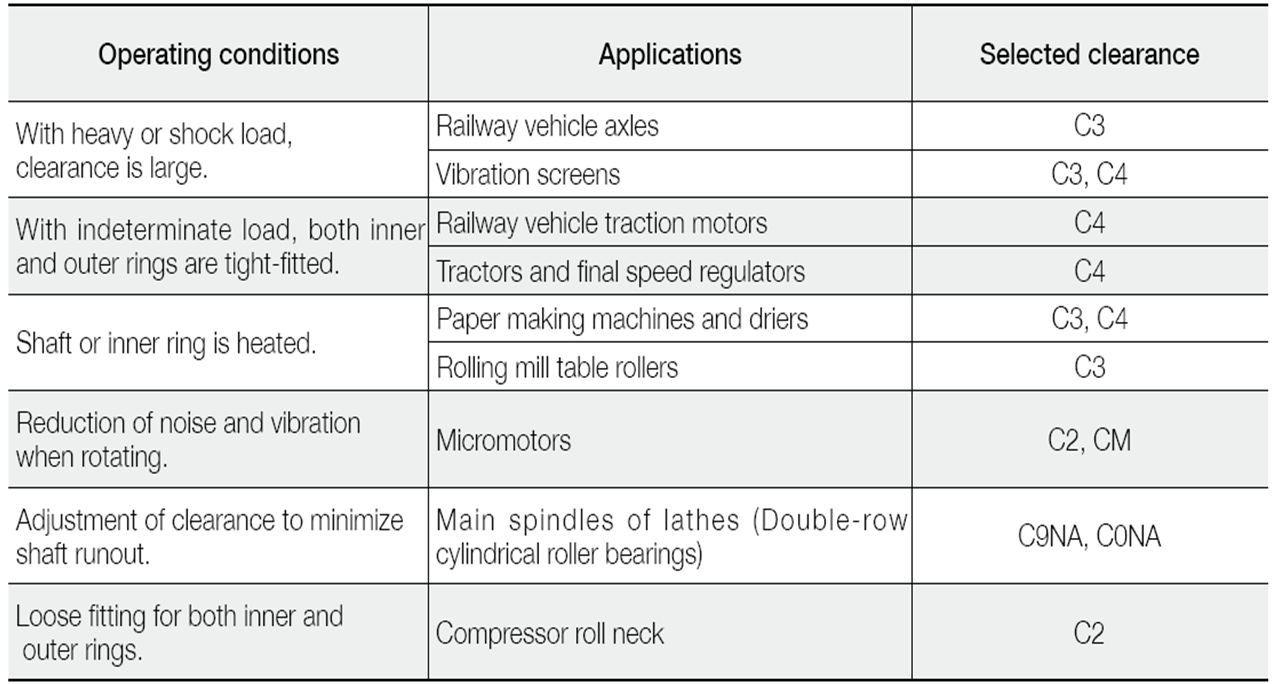
Table 2 Radial Internal Clearance of Deep Groove Ball Bearings
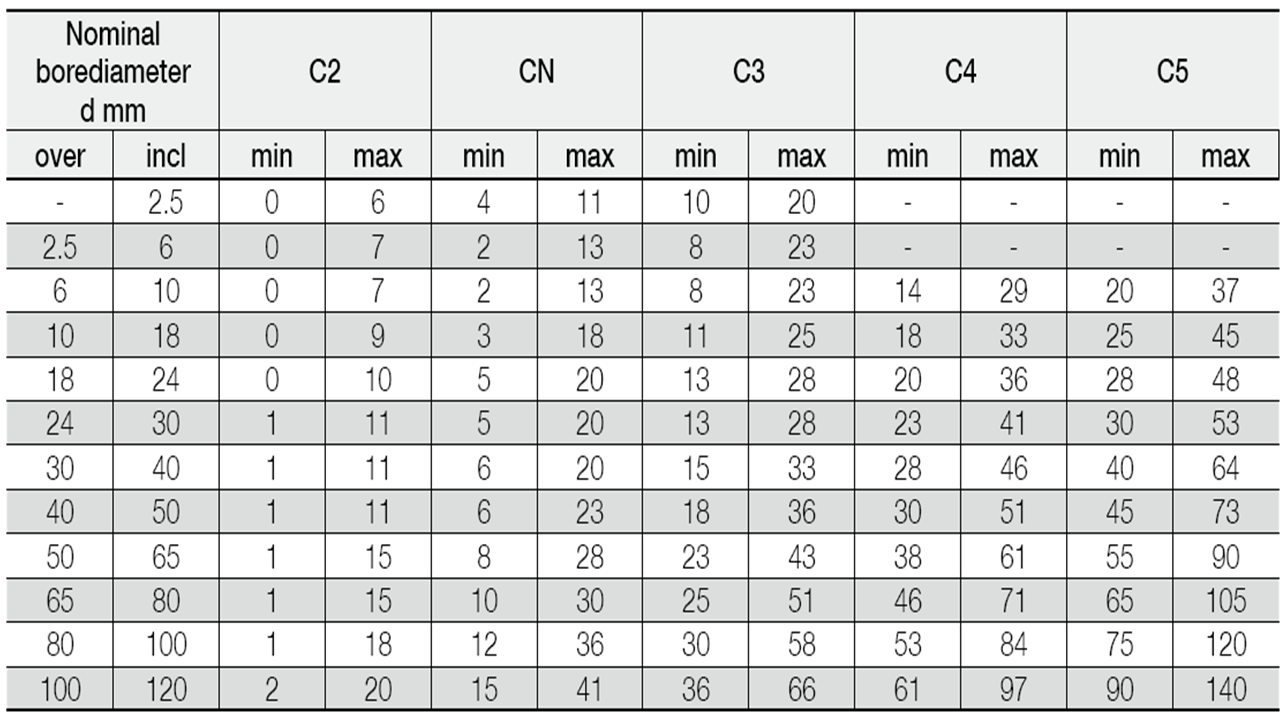
Table 3 Classification of Extra Small and Miniature Ball Bearings

Table 4 Radial Internal Clearance in Extra Small and Miniature Ball Bearings
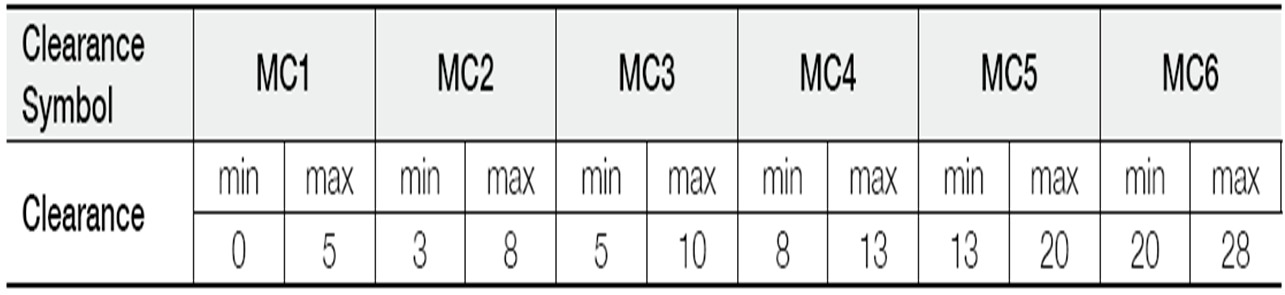
Remark: 1) The standard clearance is MC3
2) To obtain the measured value, add correction amount in the table below.
Table 5 Radial Internal Clearance of Bearings for Electric Motor
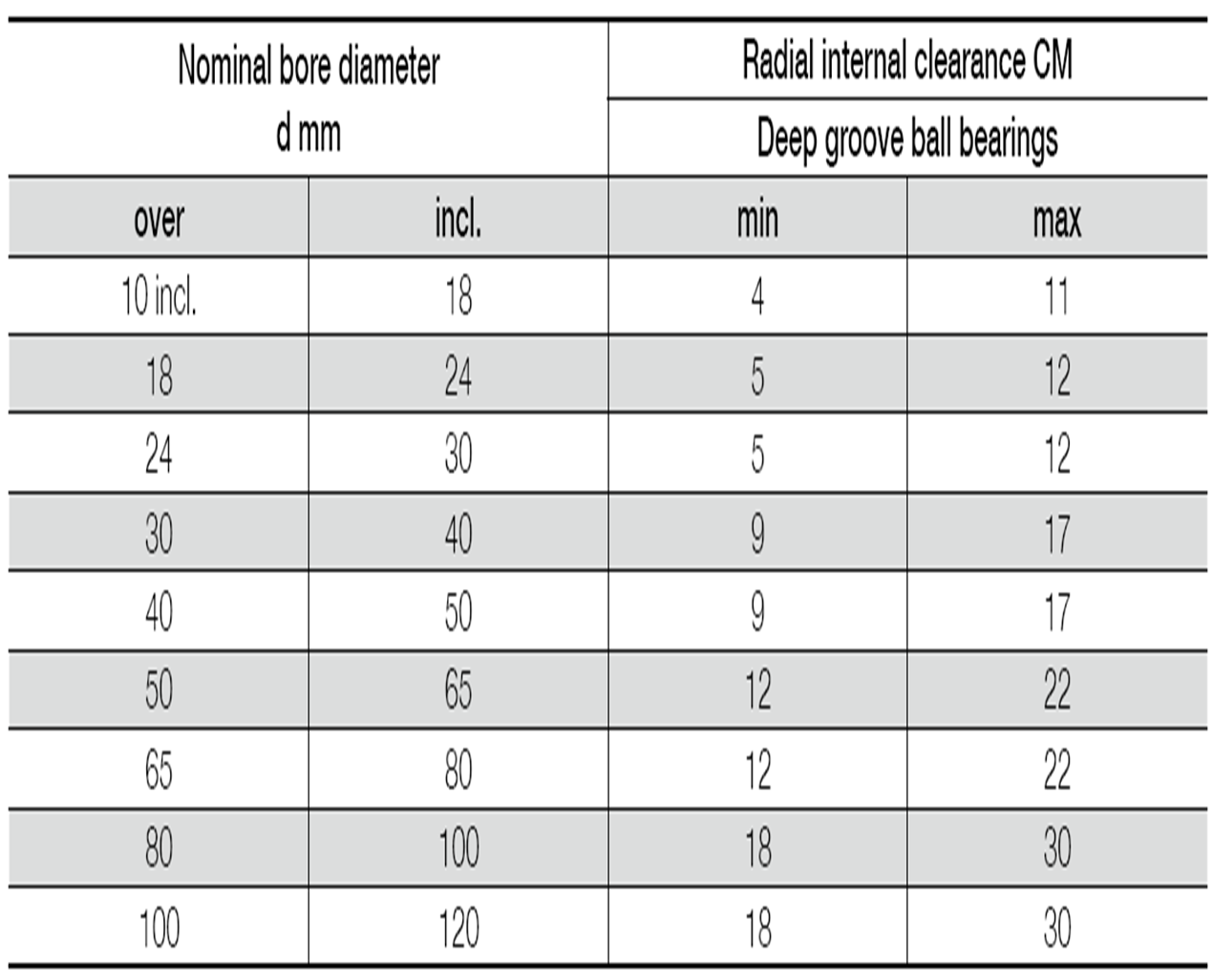
Note 1. Suffix CM is added to bearing numbers.
Example: 6205ZZCM
2. Clearance not interchangeable for cylindrical roller bearings.
- Q The Structure And Characteristics of Roller Bearings
- A
Structure and Classification
Roller bearing is commonly composed of ring, roller, cage. It is devided into ball bearing and roller bearing according to the rolling category. Apart from open type, it also has the bearing with steel shield, e.g. 608ZZ, and bearing with rubber seal ring, e.g. 608-2RS. Below diagram shows structure of roller bearing.
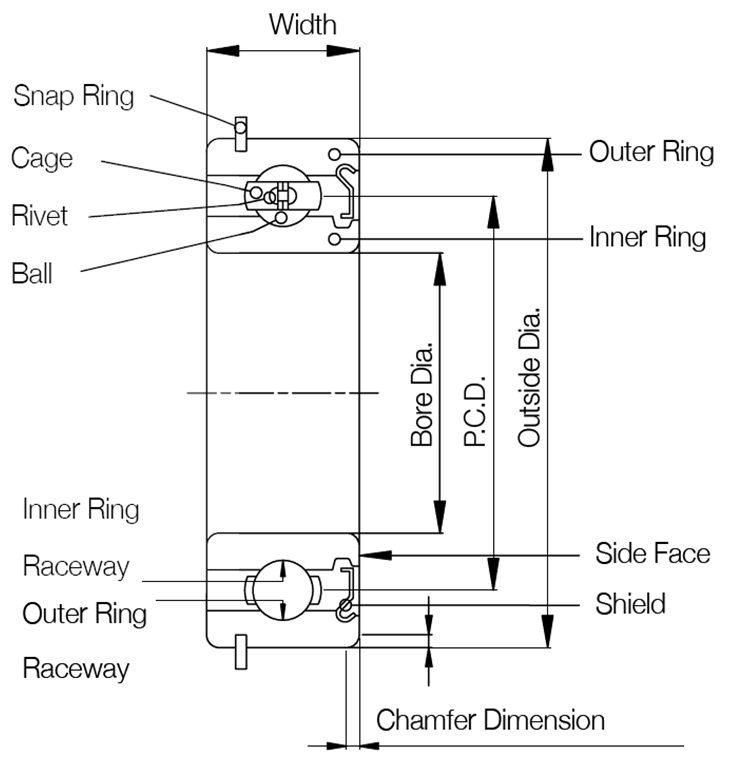
Features
The rolling bearing has features as below:
1) It is equipped with high standard and ample specifications with fine interchangeability.
2) Commonly it can simultaneouslybear radial load and axial load.
3) it is applicable for use in high and low temperature.
4) It is fit for use in high speed conditions.
Single-row deep groove ball bearing is the structure with the widest applciation in rolling bearings.
- Q Tolerances of Bearings
- A
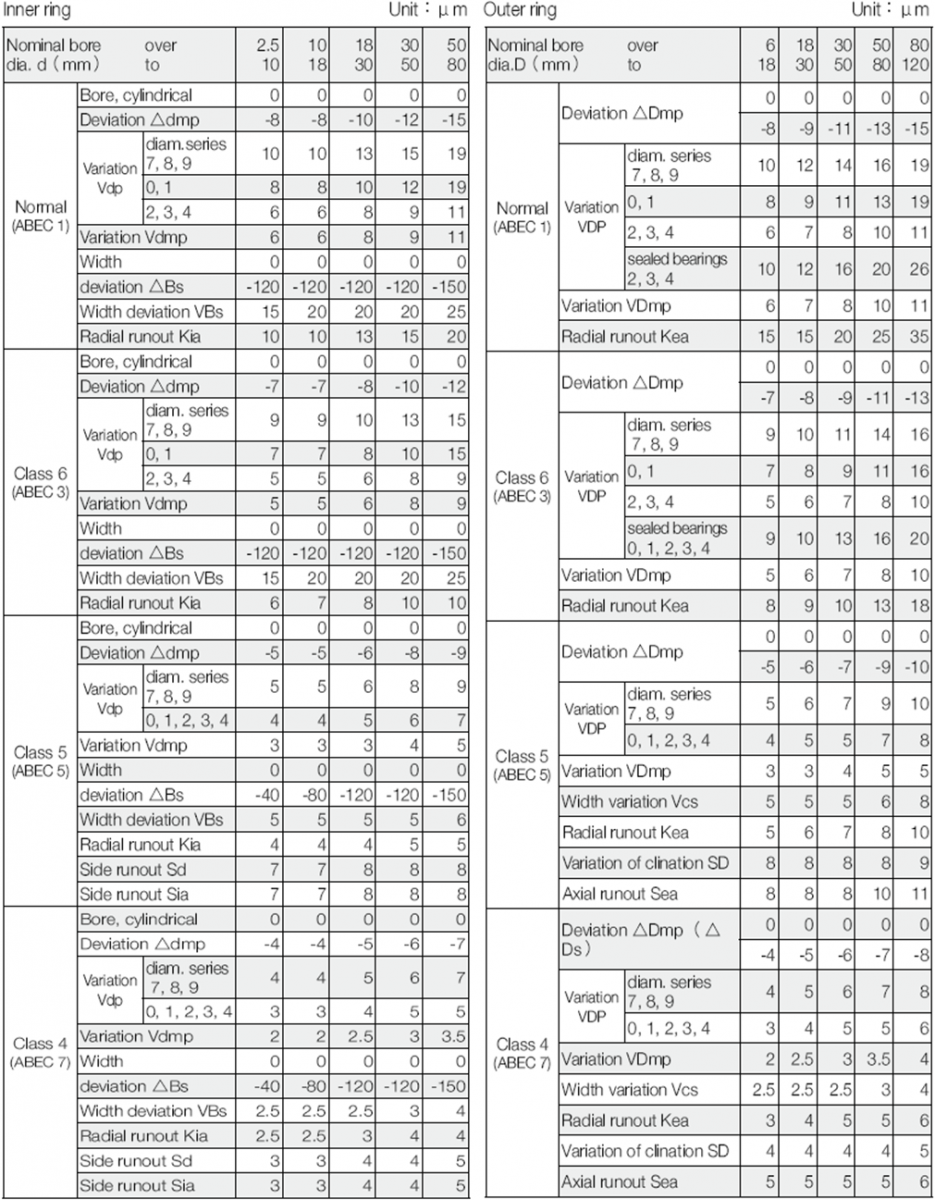
1. Tolerance Standards
The tolerances for the external dimensions and running accuracy of rolling bearings are specified by ISO 492/199/582. The applicable accuracy classes for each bearing type and the correspondence of these classes are listed in below table.
Tolerances for dimensions that are critical to mount bearings on shaft or in housing are:
1) Tolerances for bore and outside diameters, ring width and bearing width.
2) Tolerances for inscribed and circumscribed circle diameters of rollers.
3) Tolerances for chamfer dimensions.
4) Tolerances for width variation.
5) Tolerances for tapered bore diameter.
The running accuracy of rolling bearings should be specified with below items:
1) Permissible radial runout of inner and outer rings.
2) Permissible face runout with raceway and outer rings.
3) Permissible inner face runout with bore.
4) Permissible outer ring variation of outside surface generatrix inclination with face.
Tolerance Classes
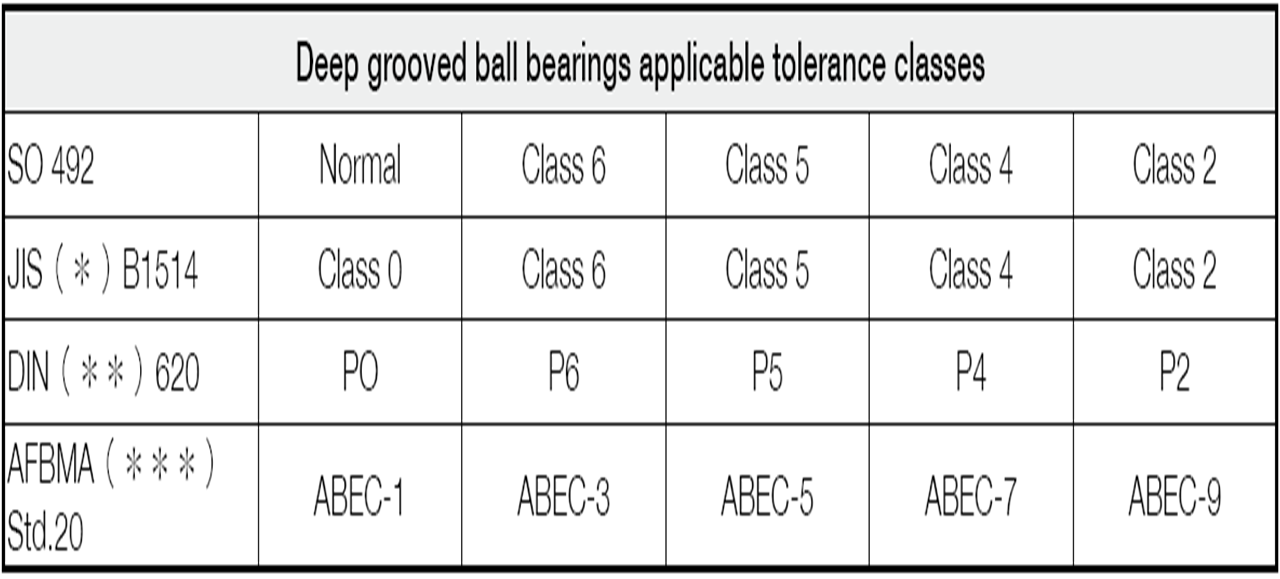
JIS: Japanese Industrial Standards
DIN: Deutsch Industrie Norm
AFBMA: Anti-Friction Bearing Manufacturers Association
2. Symbols for External Dimensions and Running Accuracy Symbols Description
d Bearing bore diameter, nominal
ds Deviation of a single bore diameter
dmp Single plane mean bore diameter deviation
Vdp Bore diameter variation in a single radial plane
Vdmp Mean bore diameter variation
B Inner ring width, nominal
Bs Deviation of a single inner ring width
VBs Inner ring width variation
Kia Radial Runout of assembled bearings inner ring
Sd Inner ring reference face (backface, where applicable) runout with bore
Sia Assembled bearing inner ring face (backface) runout with raceway
Ts Deviation of the actual bearing width
D Bearing outside diameter, nominal
Ds Deviation of a single outside diameter
Dmp Single plane mean outside diameter deviation
VDp Outside diameter variation in a single radial plane
VDmp Mean outside diameter variation
C Outer ring width, nominal
Cs Deviation of a single outer ring width
Vcs Outer ring width variation
Kea Radial runout of assembled bearing outer ring
SD Variation of bearing outside surface generatrix inclination with outer ring reference face
(backface)
Sea Assembled bearing outer ring face (backface) runout with raceway
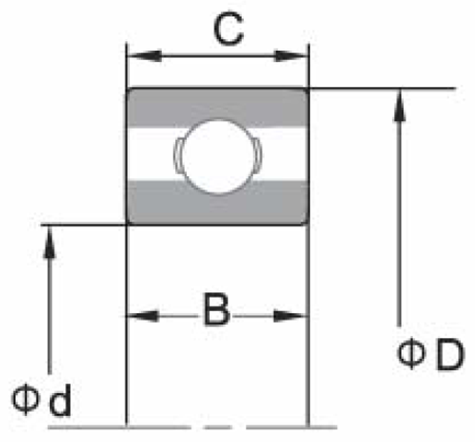
Tolerances of Radial Ball Bearings